KJ8056: Kjemiske og biologiske sensorer / Chemical Sensors and Biosensors
This subject is tought at Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Department of Chemistry, NO-7491 Trondheim, NORWAY
Course Details
Lectures: Fall semester, 2 hours
a week. Teaching language: English. Oral examination. Credits: 7.5 ECTS.
Course Lecturer
Florinel
Gabriel BANICA
Tel.: +(47) 73 59 69 57
E-mail:
F.Banica(a)chem.ntnu.no
Office: Realfagbygget, Room D2-127
SITE CONTENTS
- A short presentation of the topic
- Pensum/Syllabus
- Reading Material
- Periodicals
- Web sites dedicated to Chemical Sensors
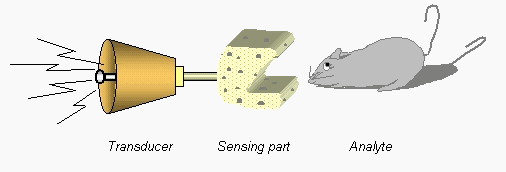
A chemical sensor is a self contained probe that provides in real time information about the chemical composition of its surroundings.
- Recognition (sensing), which consists of a specific interaction with a component of the sample (analyte). More>>
- Transduction, which represents the ensuing modification of a physical property, that can be converted into a measurable physical signal (electrical, optical, etc.). The signal is further employed for assessing the analyte concentration. More>>
What a chemical sensor looks like?
- Substitution of standard analytical procedures by fast detection and analysis using dedicated sensors;
- Automation of the analysis and monitoring of chemical quantities;
- Field analysis by means of portable instruments
- Industry: process analytical chemistry;
- Environment: automatic monitoring of chemical pollution
- Biomedical Science: fast and/or in vivo monitoring of drugs and biologically important compounds (e.g. O2, CO2 and glucose content in blood)
- Food industry and Biotechnology: automatic control of chemical parameters,such as pH, O2 and CO2 content, or nutrient concentration.
|
An application:
Measuring pH in meat
Measuring pH in slaughtered meat is
a good way to monitor product quality. A lance-shaped ISFET probe
(Sentron), with a large handle for good grip, is an ideal solution
for fast, accurate and most of all, safe measurements. More>> |
|
Main sections
Electrochemical sensors
Biosensing - General Aspects
Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors
Microgravimetric Sensors and Acoustic
Devices
Solid-state Gas Sensors
- F.G. Banica, KJ 8056: Kompendium / Lecture Notes.
- B.R. Eggins, Chemical sensors and biosensors, Wiley, New York, 2002.
- G. Ramsay (Ed.), Commercial biosensors: applications to clinical, bioprocess, and environmental samples, Wiley, New York 1998.
- D. Diamond (Ed.), Principles of chemical and biological sensors, Wiley, New York, 1998.
- T.E. Edmonds (Ed.) Chemical sensors, Blackie, Glasgow, 1988.
- J. Cooper, T. Cass (Eds), Biosensors: a practical approach, Oxford University Press, 2004.
- W. Göpel, J. Hesse and J. N. Zemel, Sensors: a comprehensive survey: VCH Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinheim. Vol. 6. Chemical and biochemical sensors. Part 1 (1991); Vol. 8: Chemical and biochemical sensors. Part 2 (1992).
- A. E. G. Cass (Ed.), Biosensors: a practical approach, IRL Press, Oxford 1990.
- F. W. Scheller and F. Schubert, Biosensors, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1992.
- A. P.F. Turner, I. Karube, and G. S. Wilson (Eds.), Biosensors : fundamentals and applications, Oxford University Press, Oxford 1987.
- A. J. Cunningham, Introduction to bioanalytical sensors, Wiley, New York, 1998.
- U. E. Spichiger-Keller, Chemical sensors and biosensors for medical and biological applications, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 1998.
Papers on chemical and biological sensors are regularly published in all the major Analytical Chemistry journals. The following journals are dedicate exclusively to this topic:
Sensors
and Actuators. B, Chemical (Elsevier Science)
Biosensors
and Bioelectronics (Elsevier Science)
Sensors
(A free, on line journal)
Potentiometric sensors
Amperometric Sensors
Semiconductor devices
Fiber Optics Sensors
Biosensors
Mass-sensitive sensors (Piezoelectric
devices)
Gas sensors
Electronic nose / Electronic
tongue
Varia
TOP^^
Copyright © 2005 by Florinel
Gabriel Banica